What is Latitude ? Discuss about the Parallels of Latitude and its types, characteristics and importance.
What is Latitude ? Discuss about the Parallels of Latitude and its types, characteristics and importance.
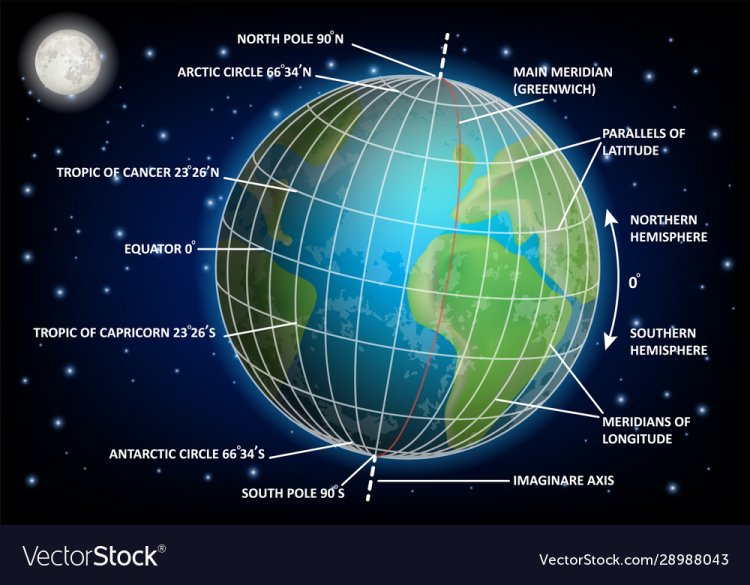
Q :- What is Latitude ? Discuss about the Parallels of Latitude and its types, characteristics and importance.
Latitude :-
The angular distance that a straight line drawn from a point on the earth's surface to the center of the earth makes with the equator along the earth's equator is called the latitude of that place. For example the latitude of Calcutta is 22°34' N means Calcutta makes an angle of 22°34' North along the equator.
Maximum value of latitude is 10° and minimum value is 0°.
Parallels of Latitude :-
Parallel imaginary lines extending from east to west parallel to the equator connecting equal latitudes on both sides of the equator are called equators.
Characteristics of Parallels of Latitude :-
1. Distribution :-
They encircle the earth from east to west.
2. Unequal length :-
Circumferences are not equal, decreases from the equator towards the poles. Maximum at the equator and zero at the two poles.
3. Circular :-
Parallels of Latitude are imaginary lines of a circle and the sum of the angles is 360°.
4. Parallel :-
Parallels of Latitude are parallel to the equator and to each and everyone. So mutual distance between them is always equal.
5. Center point :-
Their center point is at the Earth's pole. So they are miniatures. Only the center point of the equator is at the center of the earth. So the equator is the ellipse. Other than the equator, the radius of the axes is less than that of the Earth.
6. Number and value :-
179 Parallels of Latitude are visualized at 1° intervals. The maximum value of the axis is 89° and the minimum value.
7. Latitude :-
All the places on the earth located on the same equator have the same latitude.
8. Intermediate Distance :-
The distance between any two Parallels of Latitude is always equal as the Parallels of Latitude are parallel to each other.
The principal Parallels of Latitude of the earth are —
(1) Equator :-
The largest circular imaginary line that encircles the earth from east to west is located right in the middle of the earth at equal distance from the equator and the equator, is called equator. The center of the earth and the center of the equator are at the same point. So its value is 0°.
(2) Tropic of Cancer :-
The circular imaginary line that encircles the Earth from east to west, located at an angular distance of 23 ½ ° North of the equator, is called the Tropic of Cancer. And its value is 23 ½ ° North.
(3) Tropic of Capricorn :-
The circular imaginary line that encircles the Earth from east to west, located at an angular distance of 23 ½ ° South of the equator, is called the Tropic of Capricorn. Its value is 23 ½ ° South.
(4) Arctic Circle :-
The circular imaginary line located at 66 ½° angular distance North from the equator is called Arctic Circle .
(5) Antarctic Circle :-
The circular imaginary line located at 66 ½° angular distance South from the equator is called Antarctic Circle .
Importance and use of Parallels of Latitude :-
(1) Determination of position :-
How far north or south of the equator a place or region of the world can be found. The equator divides the earth into Southern and Northern hemispheres.
(2) Concept of Climate :-
As the angle of incidence of sunlight decreases north and south of the equator, altitude decreases. The length of day and night decreases. Therefore, the nature of climate of a region is known with the help of Parallels of Latitude.
(3) Boundaries :-
Parallels of Latitude define the political boundaries of a country or state. For example, 48°N is the border between Canada and the United States, 10°N is the border between Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
(4) Determination of position :-
How far north or south of the equator a place on the earth's surface is, that is, how much angular distance it is located. Again, the latitude of a place is known with the help of the axis.
(5) Local Time :-
Local time changes due to variation in the sun's declination angle with latitude.
(6) Determination of thermosphere :-
As latitude increases, the angle of incidence of the sun's rays varies, and the farther North or South one goes from the equator, the more obliquely the sun's rays fall. As a result, there are three thermospheres on Earth; Namely— (a) Torrid zone (0°-23½° N and S), (b) Temperate zone (23½°-66½° N and S), (c) Frigid zone (662½°-90° N and S).














